Therapeutic Drug Monitoring of Aminoglycosides
- May 25, 2022
Aminoglycosides (gentamicin, tobramycin and amikacin) are bactericidal antibiotics used to treat infections caused by Gram-negative organisms. Therapeutic drug monitoring is recommended to ensure adequate dosing and prevent adverse effects such as nephrotoxicity and ototoxicity. Aminoglycosides demonstrate concentration-dependent bactericidal activity, which is optimal when the maximum concentration (Cmax) is ≥ 10 times the minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) of the organism. A MIC of 1 mg/L can be assumed for most organisms; however, higher MICs (e.g. ≥ 2 mg/L) are common with Pseudomonas aeruginosa. These peak concentrations correspond to an area under the concentration-time curve (AUC24) of 70-100 mg/L.h for gentamicin and tobramycin. Prolonged high AUC24 and minimum concentrations (Cmin) are more likely to cause toxicity.
Pharmacokinetic/Pharmacodynamic Targets* |
|
| Gentamicin or tobramycin | 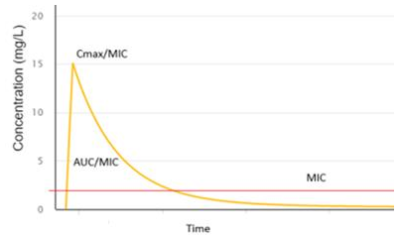 |
| AUC24: 70-100 mg/L.h Cmax: 15-30 mg/L Cmin: < 1 mg/L |
|
| Amikacin | |
| AUC24: 160-200 mg/L.h Cmax: 30-60 mg/L Cmin: < 2 mg/L |
|
| *For adult patients receiving once daily dosing, and excluding those with endocarditis | |
|
For a comprehensive guide on therapeutic drug monitoring for both aminoglycosides and vancomycin see Training workbook for therapeutic drug monitoring of aminoglycosides and vancomycin 6th edition.pdf

 Download PDF
Download PDF