| fe is the abbreviation for fraction of drug excreted unchanged in the urine. For predominantly renally cleared drugs (fe > 0.5), dose adjustment should be considered in relation to impairment of renal function (creatinine clearance/eGFR). |
- For general advice, see Individualising Drug Therapy.
- Assess renal function using estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) or creatinine clearance (CrCl).
- Consider reducing maintenance doses of medicines that are predominantly renally cleared (those with fe > 0.5) in relation to impairment of renal function.
- Loading doses are not affected.
- Consider therapeutic drug monitoring (TDM)where available to assess dose adjustment.
- When renal function is < 30 mL/min, preferentially use metabolised medicines over renally cleared medicines.
- For acute kidney injury, there are other factors to consider, such as severity and nature of the injury, and time course.
| Pharmacokinetic Considerations |
For medicines that are renally cleared i.e. fe > 0.5.
- Choose the maintenance dose, i.e. dose and frequency that you would use in this patient if renal function was normal (CrCl 100 mL/min).
- Calculate the patient’s creatinine clearance (CrCl) using the Cockcroft and Gault calculator.
Alternatively the estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) supplied by the laboratories can be used for patients whose BSA is close to 1.73m2.
Use this method to adjust the eGFR for body surface area.
3. Calculate maintenance dose:
- In patients with renal dysfunction, it is important to dose adjust to reduce the risk of adverse effects. This is more important for some medicines than others.
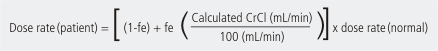
- For drugs with fe ≥ 0.9, use this equation(assume normal CrCl of 100 mL/min):

- For drugs with fe < 0.9, use this equation:
| Pharmacodynamic Considerations |
- Water and electrolyte handling may be significantly altered (e.g. increasing the likelihood of oedema, hyponatraemia, and hyperkalaemia).
- Nephrotoxic drugs (e.g. non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs) may aggravate already impaired kidneys.
| Medicines for which dose adjustment should be considered in chronic kidney disease |
| Note: Maintenance doses should be adjusted to achieve similar concentrations to that which would occur with standard doses in the setting of normal renal function. Adjustment of maintenance doses includes changes to dose, frequency or both (e.g. smaller dose, reduced frequency). The following is not an exhaustive list. These have been selected from a list of commonly prescribed medicines on the basis of having a high fe (fraction excreted unchanged in urine), or a moderate fe and low therapeutic index. Nephrotoxicity is not a factor for inclusion in this list. |
| Drug (active metabolite) |
fe, fraction excreted unchanged in urine |
Location of more detailed guidance |
Drug (active metabolite) |
fe, fraction excreted unchanged in urine |
Location of more detailed guidance |
| aciclovir |
0.8 |
|
gabapentin |
0.9 |
|
| allopurinol (oxypurinol) |
0 (0.8) |
Hospital HealthPathways |
ganciclovir |
0.9 |
|
| amoxicillin |
0.9 |
|
gemfibrozil |
0.6 |
|
| atenolol |
0.9 |
|
gentamicin |
0.9 |
Pink Book |
| baclofen |
0.8 |
|
imipenem |
0.7 |
|
benzylpenicillin
|
0.8 |
|
lamivudine |
0.8 |
|
| bezafibrate |
0.4
|
|
levetiracetam |
0.7 |
|
| bisoprolol |
0.5
|
|
lisinopril |
0.9 |
|
| candesartan |
0.6
|
|
lithium |
1 |
|
captopril
|
0.5 |
|
meropenem |
0.7 |
|
| cefaclor |
0.7
|
|
metformin |
0.9 |
|
| cefalexin |
0.9
|
|
methotrexate |
0.9-0.5 (saturable) |
|
cefazolin
|
0.9 |
|
morphine (m-6-glucuronide) |
0 (0.9) |
Hospital HealthPathways |
| cefepime |
0.8
|
|
nadolol |
0.8 |
|
cefotaxime
|
0.7 |
|
nicotinic acid |
0.4 |
|
| ceftazidime |
0.9
|
|
pethidine (norpethidine) |
0 (0.9) |
|
ceftriaxone
|
0.5 |
|
phenoxymethylpenicillin |
0.9 |
|
| cefuroxime |
0.9 |
|
piperacillin |
0.8 |
|
| cetirizine |
0.7 |
|
pravastatin |
0.5 |
|
| cilazapril (cilazaprilat) |
0 (0.9) |
|
quinapril (quinaprilat) |
0 (0.9) |
|
ciprofloxacin
|
0.5
|
|
rivaroxaban |
0.4 |
Hospital HealthPathways |
| clonidine |
0.6 |
|
sotalol |
0.9 |
|
colchicine
|
0.3
|
|
teicoplanin |
0.8 |
|
| dabigatran |
0.8 |
Hospital HealthPathways |
tobramycin |
0.9 |
Pink Book |
digoxin
|
0.8
|
Hospital HealthPathways |
tramadol (O-desmethyltramadol (M1)) |
0.2 (0.9) |
|
| doxycycline |
0.4 |
|
tranexamic acid |
0.9 |
|
enalapril (enalaprilat)
|
0.2 (0.8)
|
|
valganciclovir |
0.8 |
|
| enoxaparin |
0.7 |
Hospital HealthPathways |
vancomycin |
0.9 |
Pink Book |
ethambutol
|
0.8
|
|
varenicline |
0.9 |
|
| flecainide |
0.3 |
|
|
|
|
| flucloxacillin |
0.7 |
|
|
|
|
| fluconazole |
0.8 |
|
|
|
|


